WHY
Drivers & Context: the socioeconomic, cultural and infrastructural factors that shape how children encounter and use digital technologies.

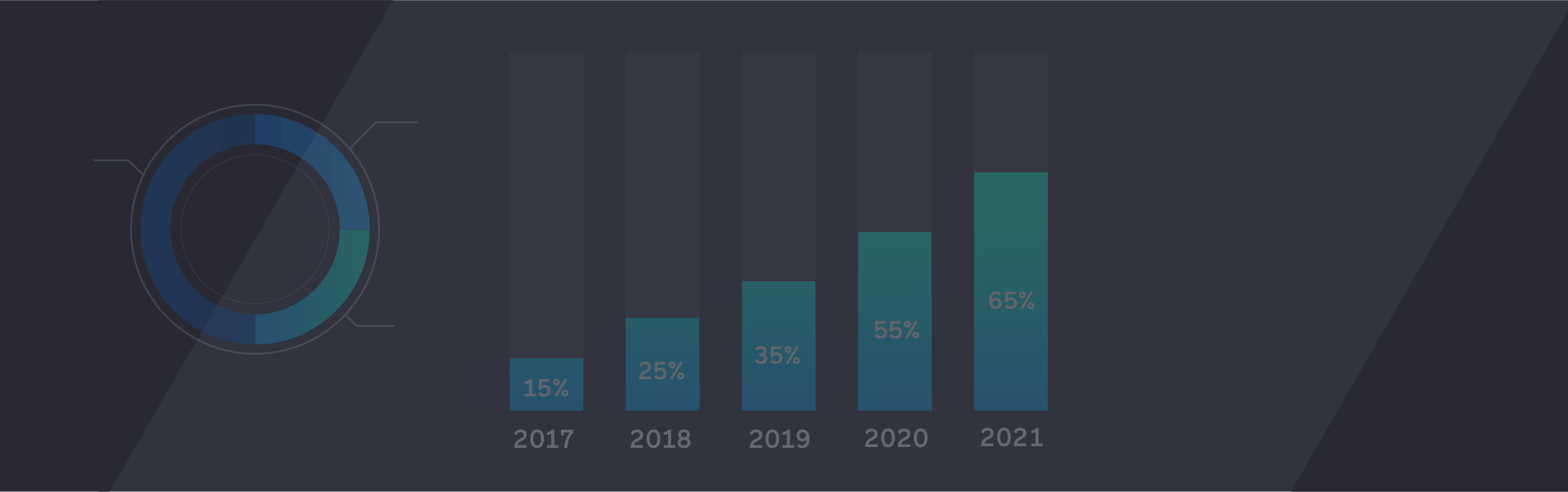
Adolescent Exposure and Usage Intensity on Social Media

Digital Divide in Children's Screen Time by Socioeconomic Status

Social Media Platforms Used by Young Users for Political and Social Information
CLINICAL
User Impact & Harm: clinical and epidemiological evidence on how social media affects the mental health, safety and well-being of children.

Age Demographics of Victims (2023-2024)

Gender Disparity in Social Media Use and Mental Health

Global Scaling of Child Sexual Abuse Material (CSAM)
STRUCTURAL
Platform Design & Dynamics: how the architecture, algorithms and business models of social media platforms create or amplify risks for young users.
TECHNICAL
Feasibility & Enforcement: the technical mechanisms, challenges and limitations of implementing age verification, content moderation and platform regulation.

Common Age Restrictions on Social Media Platforms
NORMATIVE
Rules, Rights & Ethics: public opinion, legal frameworks, generational attitudes and ethical considerations surrounding children's digital rights and regulation.

Awareness of Fundamental Rights Applied Online

Generational Perspectives on Device vs. Content Bans

Global Public Sentiment on Social Media Bans for Under-14s
MITIGATION
Alternatives & Solutions: evidence-based interventions, digital literacy programmes, platform safety features and policy approaches that reduce harm without eliminating access.